- 1 Mole Number Avogadro
- 1 Avogadro Number Definition
- 1 Avogadro Numbers
- 1 Avogadro Number
- 1 Divided By Avogadro Number
This question requires an understanding of what avogadro's number actually represents. Avogadro's number, 6.022. 10 23 is the number of things in one mole. The question indicates that there is 1 mole of H 2. Thus there are 6.022. 10 23 molecules of H 2. (One atomic mass unit = 1.66 × 10-22 g.) The number of atoms or molecules in one mole of an element or compound has been named Avogadro's number, in honor of his realization about the numbers of particles in gases. As stated above, that number has been determined to be 6.0225 × 10 23.
Related Topics:More Lessons for Chemistry
Math Worksheets
Mole, Mass & Avogadro Constant
- An amount of substance containing 6.02 × 1023 particles is called a mole (often abbreviated to mol).
- 6.02 × 1023 is called the Avogadro Constant or Avogadro's Number.
Example:
One mole of carbon contains 6.02 × 1023 of carbon atoms.
One mole of oxygen contains 6.02 × 1023 of oxygen molecules
- The mass of one mole of a substance is called the molar mass.
- The molar mass of a substance is equal to its relative formula mass in grams.
What is the mass of 1 mole of carbon?
Solution:
The mass of 1 mole of carbon = relative formula mass of carbon = 12 grams
What is the molar mass of calcium carbonate (CaCO3)?
Solution:
Step 1: Look up the relative atomic masses of the atoms from the periodic table.
Relative atomic mass (rounded to the nearest whole number):
Ca = 40, C = 12, O = 16
Step 2: Calculate the relative formula mass.
Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) contains one calcium atom, one carbon atom and three oxygen atoms.
Relative formula mass = 40 + 12 + (3 × 16) = 100
Step 3: Express the relative formula mass in grams per mole.
The molar mass of ethanol is 100 g/mol
Example:
What is the molar mass of ethanol (C2H5OH)?
Solution:
Step 1: Look up the relative atomic masses of the atoms from the periodic table.
Relative atomic mass (rounded to the nearest whole number):
H = 1, C = 12, O = 16
Step 2: Calculate the relative formula mass.
Ethanol (C2H5OH) contains two carbon atoms, six hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
Relative formula mass = (2 × 12) + (6 × 1) + 16 = 46
Step 3: Express the relative formula mass in grams per mole.
The molar mass of ethanol is 46 g/mol
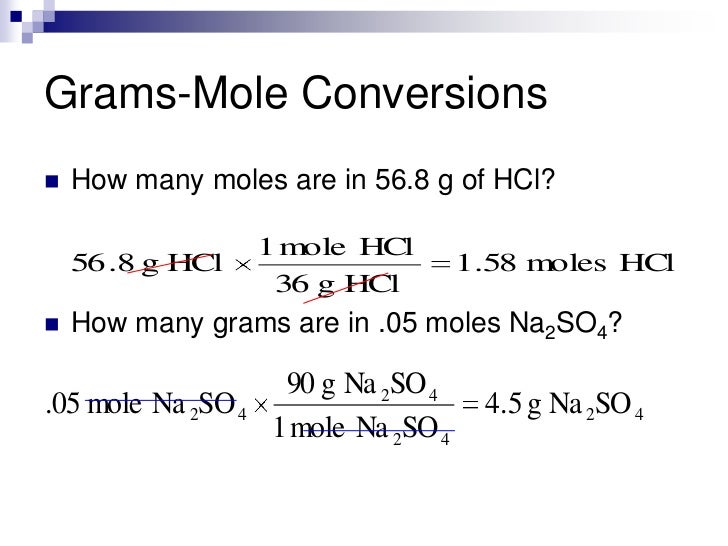
What are moles and why they are important?
How to abbreviate the mole number (Avogadro's number) using scientific notation, and compare to see how giant this number is.
- Show Step-by-step Solutions
How to convert between moles and the number of atoms or molecules using both a common sense approach, and a standard conversion factor method?
1 Mole Number Avogadro
How to round our answers with scientific notation and significant figures?
Example:
How many atoms in 5.5 moles?
How many moles is 4.6 × 1024 sulfur atoms? Converting between Moles, Atoms, and Molecules (Part 2)
More practice problems, converting between moles, atoms, and molecules.
 Example:
Example:How many molecules is 0.63 moles of molecules?
How many moles is 3.9 × 1020 Magnesium atoms?
- Show Step-by-step Solutions
The mole and Avogadro's number | Atoms, compounds, and ions | Chemistry
- Show Step-by-step Solutions
Try the free Mathway calculator and problem solver below to practice various math topics. Try the given examples, or type in your own problem and check your answer with the step-by-step explanations.
We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.
Avogadro's number is the number of particles in one mole of any substance. Its numerical value is 6.02225 × 1023. One mole of oxygen gas contains 6.02 × 1023molecules of oxygen, while one mole of sodium chloride contains 6.02 × 1023sodium ions and 6.02 × 1023 chloride ions. Avogadro's number is used extensively in calculating the volumes, masses, and numbers of particles involved in chemical changes.

1 Avogadro Number Definition
The concept that a mole of any substance contains the same number of particles arose out of research conducted in the early 1800s by the Italian physicist Amedeo Avogadro (1776-1856). Avogadro based his work on the earlier discovery by Joseph Gay-Lussac that gases combine with each other in simple, whole-number ratios of volumes. For example, one liter of oxygen combines with two liters of hydrogen to make two liters of water vapor.
1 Avogadro Numbers
Avogadro argued that the only way Gay-Lussac's discovery could be explained was to assume that one liter of any gas contains the same number of particles as one liter of any other gas. To explain the water example above, he further hypothesized that the particles of at least some gases consist of two particles bound together, a structure to which he gave the name molecule.
The question then becomes, 'What is this number of particles in a liter of any gas?' Avogadro himself never attempted to calculate this. Other scientists did make that effort, however. In 1865, for example, the German physicist J. Loschmidt estimated the number of molecules in a liter of gas to be 2.7 × 1022. The accepted value today is 2.69 × 1022.
For all elements and compounds, not just gases, a given weight must contain a certain number of atoms or molecules. A weight (in grams) equal to the atomic or molecular weight of the substance-that is, one mole of any element or compound-must contain the same number of atoms or molecules, because there is always a constant relationship between atomic weights and grams. (One atomic mass unit = 1.66 × 10-22 g.) The number of atoms or molecules in one mole of an element or compound has been named Avogadro's number, in honor of his realization about the numbers of particles in gases. As stated above, that number has been determined to be 6.0225 × 10 23.
1 Avogadro Number
See also Atomic weight.
Additional topics
1 Divided By Avogadro Number
Science EncyclopediaScience & Philosophy: A-series and B-series to Ballistic Missiles - Categories Of Ballistic Missile
